Demystifying Web3
The three epochs of the Internet: 1. Web, 2. Mobile, 3. Blockchains
DNS is somewhat decentralized. Web3 brings a better version to more apps.
Introduction
Web 3.0 is the latest Internet technology that leverages machine learning, artificial intelligence and blockchain to achieve real-world human communication. The icing on the cake is that web 3.0 not only allows individuals to own their data, but they will be compensated for their time spent on the web.
What Is Web 3.0?
Table of contents
- What Is Web 3.0?
- Difference Between Web 1.0, Web 2.0 and Web 3.0
- How Does Web 3.0 Work?
- Advantages of Web 3.0
- Disadvantages of Web 3.0
- Why Web 3.0 Is Important for the Future
- Examples of Web 3.0 Applications
- Web 3.0 and Blockchain
- Web 3.0 and Digital Marketing
- Web 3.0 and Metaverse
- Web 3.0 FAQs
Decentralization, openness and incredible user utility are the defining characteristics of web 3.0.
A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) is an automated computer network organization model controlled by its community members rather than a single establishment like the government or a financial institution, and whose transaction records are maintained on a blockchain.
The idea behind using the semantic web is that it understands and interprets the context and concept of the data. Therefore, when a user searches for an answer, web 3.0 delivers the most accurate and relevant result to the end-user.
Tech giants such as Google, Facebook and Microsoft are some of the few companies currently making an enormous profit from user data. But web 3.0 will enable all of us to be compensated for our time and data:
“People have been exploited by tech firms — essentially, deceived into giving valuable data away with little or no compensation from the firms who collect and benefit from it. Instead, [with web3] people should be paid for the data they share.”
This means that users will be able to sell their own data to advertisers while still retaining ownership and data privacy. In addition, web3 will enable websites and applications to use data more meaningfully and tailor the information to each user.
Hence, this third evolution of the web is an Internet where you will enjoy personalized interactions with machines and websites in the same manner as when you communicate with any other human.
Key Features of Web 3.0
The key features of web 3.0 are:
- Open – It’s ‘open’ in the sense that it’s made with open-source software developed by an open and available community of developers and accomplished in full view of the public.
- Trustless – The network offers freedom to users to interact publicly and privately without an intermediary exposing them to risks, hence “trustless” data.
- Permissionless – Anyone, including users and providers, can engage without the need for permission from a controlling organization.
- Ubiquitous – Web 3.0 will make the Internet available to all of us, at any time and from any location. At some point, Internet-connected devices will no longer be limited to computers and smartphones, as they are in web 2.0. Because of the IoT (Internet of Things), technology will enable the development of a multitude of new types of intelligent gadgets.
How Does Web 3.0 Work?
The idea behind web 3.0 is to make searches on the Internet much faster, easier and more efficient to process even complex search sentences in no time.
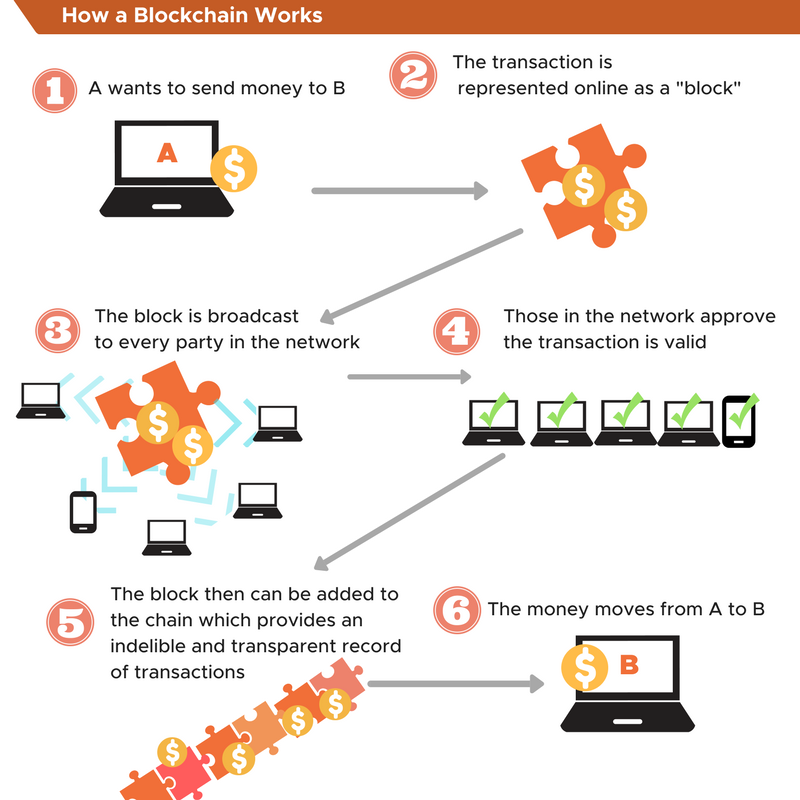
In a web 2.0 application, a user has to interact with its frontend, which communicates to its backend, which further communicates with its database. The entire code is hosted on centralized servers, which are sent to users through an Internet browser.
Web 3.0 has neither centralized databases that store the application state nor a centralized web server where the backend logic resides. Instead, there is a blockchain to build apps on a decentralized state machine and maintained by anonymous nodes on the web.
The logic of your applications is defined in smart contracts, written by the developers, which are deployed onto the decentralized state machine:
Anyone willing to build a blockchain application deploys their code on this shared state machine. The front end remains almost the same as in web 2.0.
Here is a figure depicting the working of a web 3.0 application:

Web 3.0 Architecture
There are primarily four elements in the architecture that make up web 3.0:
- Ethereum Blockchain – These are globally accessible state machines maintained by a peer-to-peer network of nodes. Anyone in the world can access the state machine and write to it. Essentially, it is not owned by any single entity but, rather, collectively by everyone in the network. Users can write to the Ethereum Blockchain, but they can never update existing data.
- Smart Contracts – These are programs run on the Ethereum Blockchain. These are written by the app developers in high-level languages, such as Solidity or Vyper, to define the logic behind the state changes.
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) – The purpose of these machines is to execute the logic defined in the smart contracts. They process the state changes taking place on the state machine.
- Front End – Like any other application, the front-end defines the UI logic. However, it also connects with smart contracts that define application logic.
Advantages of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 will make the web more intelligent, secure and transparent, resulting in more efficient browsing and effective machine-human interaction.
Here are the top advantages of the semantic web or web 3.0:
- Data Privacy and Control
The end-users will get the most significant advantage of data encryption to protect their information from disclosure.
The encryption will be unbreakable in any given circumstance. It will prevent large organizations like Google and Apple from controlling or using people’s personal information for their own interest.
Hence, users will gain complete ownership and privacy of their information.
Dive Deeper: Google Privacy Sandbox: What Does It Mean for the Future of Targeted Ads?
- Seamless Services
Decentralized data storage will ensure that the data is accessible to users in any circumstance. Users will get multiple backups, which benefits them even in the event of server failures.
Additionally, no entity or government organization will have the ability to stop any services or websites. Therefore, the possibility of account suspension and denial of distributed services will be reduced.
- Transparency
Regardless of which blockchain platform end-users use, they will track their data and inspect the code behind the platform.
Nonprofits develop the majority of blockchain platforms, which means they provide an open-source blockchain platform that allows open design and development processes. This will help eliminate the dependency of users on the organization that develops the platform.
- Open Accessibility to Data
The data will be accessible from anywhere and from any device. The idea is to increase data collection and its accessibility to users worldwide by allowing smartphones and other connected devices to access data on the computer if synced.
Web 3.0 will further expand the scale of interaction, ranging from seamless payments to richer information flows to trusted data transfers. This will happen because web3 will enable us to interact with any machine without passing through fee-charging middlemen.
- Restrictionless Platform
Since the blockchain network is accessible to all, users can create their own addresses or interact with the network.
Users cannot be restricted on this network based on their gender, income, geographical location or sociological factors. This feature will make it easier for users to transfer their assets or wealth anywhere across the world in no time.
- Single Profile Creation
With web 3.0, users do not need to create individual personal profiles for different platforms. A single profile will work on any platform, and the user will have complete ownership of any given information.
Without users’ permission, no corporation can access their data or verify its accuracy. However, users have the choice to share their profiles and sell their data to advertisers or brands.
- Enhanced Data Processing
Web 3.0 is beneficial for problem-solving and intensive knowledge creation tasks. It utilizes artificial intelligence to filter out valuable information from a huge quantity of data.
Users will also benefit from its ability to conduct client demand forecasting and personalized customer service, necessary for flourishing businesses.
Embrace Decentralized Web
Disadvantages of Web 3.0
There are also several challenges associated with the implementation of web 3.0. Personal data management and reputation management issues will become more critical than ever.
Here are the top challenges associated with the implementation and usage of web3:
- Requires Advanced Devices
Less advanced computers won’t have the ability to provide the benefits of web 3.0. The devices’ features and characteristics will need to be extended to make the technology reachable to more people globally. Considering the present scenario, only a limited number of people will be able to access web 3.0.
- Web 1.0 Websites Will Become Obsolete
If web 3.0 becomes full-fledged on the Internet, any websites based on web 1.0 technology will become obsolete. The old technology is incapable of updating its features to match the new ones. This means those sites will be substantially more outdated and consequently lose a competitive edge over new sites.
- Not Ready for Widespread Adoption
Web3 technology is more intelligent, efficient and accessible. Yet, the technology is not entirely ready for widespread adoption. Much work is needed on technology advancement, privacy laws, and data use to satisfy the user’s needs.
- Demand for Reputation Management Will Increase
With the easy availability of a user’s information and less anonymity through web 3.0, reputation management will become a matter of concern more than ever. In other words, brands and companies will need to maintain their name, reputation and image online.
Companies will need to help customers acquire critical market intelligence, valuable business insights, compelling content and cutting edge internet marketing to stay ahead of competitors. Hence, reputation management will turn out to be more critical than ever.
Dive Deeper: Best Reputation Management Companies: Top 5 Choices for 2023
- Complicated Functionality
Web 3.0 is a difficult-to-understand technology for any new user, which makes them hesitant to use it. It is a combination of older-generation web tools with cutting-edge technologies, such as AI and blockchain, as well the interconnection between users and increasing Internet usage.
This will mean that only advanced devices will be able to handle web 3.0, making it difficult for any individual or business that cannot afford such devices. Because it is technically sound users who will gain the most from this technology, the complicated nature of web 3.0 is likely to slow down its popularity at a global level.
Dive Deeper: 4 Ways to Stay Ahead of the Game: The Future of Digital Advertising in 2023 & Beyond
Why Web 3.0 Is Important for the Future
Web 3.0 is a system for users, designed by users in the form of creator-driven platforms.
Here are the top reasons why web3 will become important in the coming years:
- Less reliance on centralized repositories: Web 3.0 will attempt to make the Internet a diverse source so that hackers, leaks and reliance on centralized repositories are avoided. Using verifiable data scarcity and tokenized digital assets, there will be the possibility of users owning their own data and digital footprints. No platform will be held accountable for data usage.
- More personalized interactions: Web 3.0 will become increasingly important in 2023, as most users continue to prioritize customized and individualized browsing encounters on the web.
- Better search assistance powered by AI: There will be an increasing demand for humanized digital search assistants that are far more intelligent, pervasive and powered by semantics, blockchain and AI.
- Reduced dependency on intermediaries: It will help disintermediate businesses, remove rent-seeking intermediaries, and give this value directly to the customers and providers in a network. Network users will work together to address previously hard-to-control problems by mutual ownership and governance of these new decentralized intelligence structures.
- Rise in peer-to-peer connectivity: Through new Internet inventions, the connection between members and organizations will remain innately robust to keep in line with more adaptive peer-peer interaction and governance. With peer-to-peer connectivity, humans, businesses and machines will be able to share more data while maintaining greater privacy and security.
- Enhanced trust: With the knowledge of the next Internet generation, we can reduce dependency on individual platforms to future-proof entrepreneurial and investment activity.
Examples of Web 3.0 in Real Life
Web 3.0 is already implemented in various areas, including virtual assistance, education, social networking, messaging, exchange services, browsing, etc.
For instance, while you’re sitting in the office, if you wish to check the availability of groceries in your home, you can ask your digital assistant to examine the contents of your fridge by communicating with the interconnected smart devices at your house.
Moreover, you can organize your holiday plan, business trip, weekend party, household tasks and even ensure your home security by using your ubiquitous Internet-connected devices at home. The virtual assistant’s personalized recommendations help you arrange the perfect weekend, from booking your tickets with a discount to finding exciting places to explore to reserving hotels.
Examples of Web 3.0 Applications
Here are some popular examples of web 3.0 applications that explain the scope of its adoption:
Apple’s Siri
Siri is a perfect example of voice recognition software as a key component of web 3.0. Using this technology, Siri and other personal assistants communicate, share information (through linked blocks), and provide users with more helpful search results for every meaningful query, including how to, why, and what. Previously, Siri could accomplish only simple tasks, like reminders and directions to the local grocery store, by using pre-programmed algorithms.
Dive Deeper: Hey Siri: How Do I Optimize for Voice Search?
Wolfram Alpha
Wolfram Alpha is a computational intelligence platform that now uses web3. The platform can compute answers of users from different fields like mathematics, nutrition and science. It quickly connects with other apps to gather information from their databases and streamlines the information for end-users. As a result, it is now faster and provides more accurate results than it used to be with web 2.0. Siri is a frequent user of Wolfram Alpha.
Steemit
Steemit is a great example of web 3.0 social network websites. It is a decentralized reward platform that runs entirely on the Steem Blockchain social media model. It rewards content creators or bloggers with cryptocurrencies for contributing content on the site. This is precisely where web3 becomes vital as it helps the platform reward contributors’ crypto in a secure environment.
Sola
Another example of a web 3.0 social network website is Sola. It is a decentralized social platform powered by distributed nodes, IPFS, and the Ethereum blockchain.
Unlike Steemit, Sola utilizes blockchain AI to build social networks and media hybrids. It incentivizes and benefits all involved parties, including users, third-party developers and the core team for viral content.
The website uses AI algorithms to filter in only good content to endorse and doesn’t rely only on user reaction to spread posts. Also, Sola pays users its internal virtual currency, known as Action Points, and users can spend it on their own content or for endorsing other users’ content.
IDEX
IDEX is a renowned decentralized exchange for trading ERC-20 tokens that work on web 3.0. As IDEX is an Ethereum-based exchange, the user would need an Ethereum wallet to trade on the platform. Also, they would need to use MetaMask (a crypto wallet used to interact with the Ethereum blockchain) to get the best experience of IDEX.
e-Chat
e-Chat is a web 3.0 app that is powered by a decentralized blockchain. Essentially, it is a secure messenger, but it is also known as the fastest-growing social network. Users get the benefit of sharing any data without fearing its theft. Therefore, it is widely used to send cryptocurrency. App Store and Play Market have an e-Chat app for their users.
Storj
Decentralized storage is one of the primary features of web3, and Storj utilizes this feature wisely. It is one of the oldest and leading decentralized storage solutions, powered by blockchain technology that allows users to rent their free disk space.
Storj has a native token that is used as a payment method on the network. Users can earn based on the shared disk space paid for by the renters on the platform. The transaction is made on this platform through blockchain technology.
Everledger
Everledger is an example of insurance and banking on web 3.0. This distributed digital global registry is designed to allow users to store their data digitally and access them anytime at their convenience while ensuring their data security. Since web 3.0 has a data encryption feature, Everledger can protect the data and minimize the risk of fraud to the users, banks, open marketplace, and insurers.
LBRY
LBRY is a web 3.0 video and music website with a library of different forms of content, such as books, music and videos. The decentralized digital library uses blockchain technology to publish material and monetize it with its integrated payment system.
Ethlance
Ethlance is a web 3.0 remote job platform. The decentralized app works on top of the Ethereum blockchain, where anyone can hire and start working in exchange for Ether cryptocurrency, which was never possible with older technology.
Embrace Decentralized Web
Web 3.0 and Blockchain
Blockchain is often associated with web 3.0, and it can be difficult to understand they are the same or different.
In simple terms, blockchain is the technology (along with others like IoT and AI) behind web 3.0. More specifically, blockchain is the foundation of web3, as it redefines the data structures in the backend of the semantic web.
Blockchain, also called Ethereum blockchain,
is a decentralized state machine that deploys intelligent contracts. These smart contracts define the logic of an application for web 3.0. So anyone who wishes to build a blockchain application needs to deploy their application code on the shared state machine.
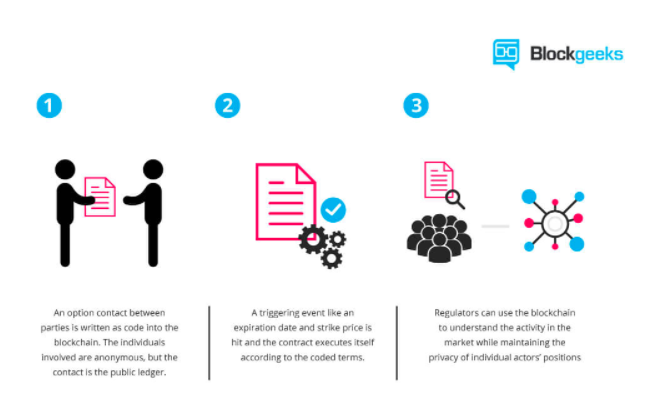
All the application data and codes are stored and managed on the blockchain, and this is collectively owned and maintained by a peer-to-peer network of nodes. The rules of agreement between the peers in the network determine the state changes on the state machine or blockchain:
All data here are globally accessible, but the existing data cannot be edited or changed. Users can send files in a copy-protected way, hence enabling actual P2P transactions without intermediaries. This means files and data are encrypted before sharing and are fully secured on web 3.0.
When a user interacts with a web 3.0 app, it utilizes AI and machine language/natural language processing to process the queries and bring the required data or information straight from the blockchain that is accessible anywhere in the world.
Dive Deeper:
* The Ultimate Guide to Blockchain Digital Marketing and Cryptocurrency
* How Blockchain Can Be Instrumental in Preventing Digital Fraud
* Will Blockchain Technology Be a Music Industry Savior?
Web 3.0 and Digital Marketing
Here are some of the ways that web 3.0 will have an impact on digital marketing:
- Less focus on keywords: In web 3.0, there will be less focus on keyword optimization. Instead of focusing on keywords, marketers must create multimedia content that understands users’ needs and queries.
- Reduction in “near me” queries: There will be a drastic decrease in “near me” queries because people know that the results will automatically be relevant to their location. Hence, they have stopped adding “near me” or zip codes to their search. Web 3.0 automatically considers the user’s geo-location and behavior data and shows relevant results that match their interest.

- Increase in voice search: Web 3.0 will lead to an increase in voice search, and people will start using digital assistants even more. Therefore, the key will be to optimize for more specific and long-tail queries.
- More significance on Microdata and of Schema: Understanding the data is more crucial on web 3.0. All marketers should embrace Microdata and Schema markup to stay ahead in the game as they help the web3 application understand the concept and context and structure the data. With a clear understanding, it will ensure that your content is shown to the user for relevant queries.
- Growth of question-keywords optimization, featured snippet optimization, and PAA (People Also Ask) section: Web 3.0 will increase question-keyword optimization, featured snippet optimization, and PAA optimization. Marketers must produce content that answers users’ questions accurately.
- Rise of hyper-personalized experiences: Web 3.0 will also replace the idea of old static websites with hyper-personalized experiences that change their messaging and their media formats for each visitor. Speaking with search engines in natural language and finding accurate information delivers a seamless user experience; the ability of web 3.0 to learn and think will emphasize this rich experience for users.
Dive Deeper:
* 38 Digital Marketing Trends You Can’t Ignore in 2023
* 12 Ways to Use Machine Learning in Digital Marketing
* Featured Snippets: How to Optimize for Position Zero
Web 3.0 and Metaverse
Metaverse is quite a buzzword since Facebook recently announced its new name ‘Meta’. The idea is to showcase that the company is moving fast towards a Metaverse. However, Metaverse is still not a reality, but soon could be the next evolution of the Internet.

Metaverse generally refers to shared virtual world environments or a computer-generated environment, which is accessible to users via the Internet. It is a digital space that is designed as more lifelike by using “extended reality,” the combination of augmented, virtual and mixed reality.
At the moment, people interact with each other through social media platforms or by using messaging applications. In the virtual space, users will have their own “character” that can walk around and interact with other users. They can communicate with one another through avatars, text messages, sounds, music videos, video games, etc.
This means that people will have a 3D experience on the Internet. They can interact, play, work, or join in digital environments as if they are experiencing it in reality rather than just watching the content.
The role of web 3. 0 is vital in making Metaverse a reality, specifically if it uses blockchain technology. In other words, web3 will enable the virtual world to exist online and be accessible through a web browser.
Presently, Metaverse is more associated with virtual gaming, but this is not limited to only games. The scope of the web 3.0 Metaverse is much broader that also includes the education industry. For example, in an education Metaverse, users can enter an immersive classroom and interact with their teacher and other students.
In the future, web 3.0 and Metaverse will together proliferate in all aspects of society.
Final Thoughts on Web 3.0
We are heading towards an Internet where people will have complete control over their data and privacy, and permit companies to use their data (or not). All this will be powered by blockchain.
Therefore, web 3.0 will accelerate the honest and transparent use of user data, from personalized search results to cross-platform development tools and the use of 3D graphics. The web will become more immersive and interactive.
The new Internet will be here soon! Let’s embrace web 3.0 with open arms.
Web 3.0 FAQs
Here are some of the commonly asked questions and their answers related to the semantic web:
How long will it take for web 3.0 to be fully implemented?
Many tools that are necessary for web 3.0 have been developed, and some are already in use. Since the concept of web 3.0, or the semantic web, is complex and has some technical difficulties, transitioning from web 2.0 will take some time to implement fully, and it may even take years.
Is web 3.0 the same as the semantic web?
Although these two terms are often used interchangeably, they are not exactly the same thing. Web 3.0 uses semantic technology, along with machine learning and blockchain, to make user interaction more intuitive.
The inventor of the World Wide Web, Tim Berners-Lee, coined the term “semantic web” and associated the semantic web with web 3.0. So, in that sense they can be said to be the same because the semantic web is one of web 3.0’s key features. It allows machines to quickly understand data and react to human queries with accurate results.
Is web 3.0 user-friendly?
Yes, web 3.0 is user-friendly because it harnesses the power of big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to analyze the user’s data and behavior to provide a personalized experience. In the web 3.0 era, you can speak with devices like Alexa, Google Echo, Apple Siri, etc., as naturally as you talk with another person to gather information from the web.
How will web 3.0 make your web experience better?
Web 3.0 will make your web experience better in three ways:
- Personalized browsing experience – Web 3.0 provides a highly personalized browsing experience for everyone. Websites will automatically adapt to your device, location, and accessibility needs.
- Better search – The utilization of machine learning and AI allows you to speak in your natural language with the search engine. It delivers the most accurate results by leveraging big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
- Richer app experiences – Web 3.0 not only enhances your website usability, it improves your app user experience, too.
What are some of the examples of web 3.0?
Wolfram Alpha and Apple’s Siri are two examples of web 3.0 applications. Siri uses speech recognition techniques and artificial intelligence to search and deliver results.
For instance, if you are a vegetarian and you ask Siri, “Best places to have dinner,” Siri will offer some good recommendations on vegetarian restaurants near your location without your having to tell it that you are a vegetarian. Siri can identify that data using your past browsing history. Hence, based on your location and behavior preferences, Siri delivers you perfect results.
| What is the advantage of web 3.0? | What are the disadvantages of web 3.0? |
|---|---|
Here are some of the benefits of web 3.0:
| Here are some of web3’s drawbacks:
|
What is the difference between web 2.0 and web 3.0?
There are plenty of things that differentiate web 3.0 from web 2.0. But one crucial factor that emphasizes web 3.0 is humanization — the ability to think. With web 2.0 (where we are now), people create and share content with others by tagging, categorizing, etc. But web 3.0 (with the semantic web, AI, and machine learning) thinks independently and connects people with the best and most accurate results.
What are web 3.0’s features?
Here are the five significant features of web 3.0:
- Semantic web
- Artificial intelligence
- 3D graphics
- Connectivity
- Ubiquity
How will web 3.0 impact businesses?
3D graphics are a great feature for a business. If you’re a product-based business, by developing a 3D product model, you can lure in your audience and improve your conversion rate.
More than that, you can use the technology to develop your business from scratch, create a digital clone for your online store, show people your manufacturing line, and plenty more. It is cost-effective and the benefits are endless.
Apart from that, web 3.0 will make businesses more transparent and highly user-centric. It opens up the gates for blockchain, and in the future, apps and websites will deploy blockchain and allow users to trade in cryptocurrencies and coins to make purchases.
Watch this video about web3 on our Leveling Up YouTube channel, where you can find tons more videos on digital marketing topics like SEO, content marketing, NFTs, web3, paid media, email marketing, growing your business, and much more!
Summary
Behind the buzzword, web3 remains very close to the classic web or web2:
- Open-source javascript frameworks like React or Vue are still used to build front-ends.
- Best practices for code quality, security, and performance are the same.
- The main difference is that the data storage is done in web3 on a blockchain instead of being stored on a centralized database.
- Immutability, open-source code and transaction fees bring new technical challenges.
- Using technology such as blockchain, web3 introduces new ownership, incentives and community models.
- New products, services and business relationships will arise from web3.
- Business leaders should begin to formulate a web3 strategy and begin experimenting with the framework.

There is an emerging tech ecosystem that promises to revolutionize physical and digital business models: web3.
Web3 is more than a singular technology. It’s more than a convergence of technologies. It’s an ethos that has the potential to empower consumers while strengthening the relationship consumers have with brands that are willing to operate with them in the space. Web3 fundamentally changes the way business takes place and how we connect to one another on a personal level. In fact, web3 is expected to fundamentally alter the way we think about our presence online over the next few years.

Web 1.0: | Read-Only (1990-2004): In 1989, at CERN, Geneva, Tim Berners-Lee was busy developing the protocols that would become the World Wide Web. His idea? To create open, decentralized protocols that allowed information-sharing from anywhere on Earth. The first inception of Berners-Lee's creation, now known as 'Web 1.0', occurred roughly between 1990 to 2004. Web 1.0 was mainly static websites owned by companies, and there was close to zero interaction between users - individuals seldom produced content - leading to it being known as the read-only web. |
Web 2.0: | Read-Write (2004-now): The Web 2.0 period began in 2004 with the emergence of social media platforms. Instead of a read-only, the web evolved to be read-write. Instead of companies providing content to users, they also began to provide platforms to share user-generated content and engage in user-to-user interactions. As more people came online, a handful of top companies began to control a disproportionate amount of the traffic and value generated on the web. Web 2.0 also birthed the advertising-driven revenue model. While users could create content, they didn't own it or benefit from its monetization. |
Web 3.0: | Read-Write-Own: The premise of 'Web 3.0' was coined by Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood shortly after Ethereum launched in 2014. Gavin put into words a solution for a problem that many early crypto adopters felt: the Web required too much trust. That is, most of the Web that people know and use today relies on trusting a handful of private companies to act in the public's best interests. |
The technical specificities of web3
Blockchain: In web3, there is no centralized entity that controls the data. Data is distributed and duplicated over thousands of “nodes” that update with a consensus mechanism. This is the principle of a blockchain.
Solidity: is the programming language for smart contracts on Ethereum. Its syntax is close to javascript. This language is in the process of imposing itself on blockchains compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
Infura and Alchemy: Infura and Alchemy are API providers that allow easy communication with reference blockchains. This speeds up development by avoiding having to maintain a blockchain node yourself.
Web3.js: Web3.js is the reference javascript library to allow a front-end to communicate with smart contracts.

The web advances
The original web (1) simply connected computers and users worldwide (hence the name World Wide Web) and is often called the “read only” internet. Web2, often called the read-write internet, broadened content and connections to encompass things like social media, real-time content/news, online shopping and more elaborate web applications. This is where we are now, where we’re all creating and sharing content on social media. But most of this data is owned and controlled by the platform companies.
Web3, often called read-write-own, represents the next big step in the evolution of online interactions. It enables a bridge between the physical and virtual worlds by introducing new ownership and transactional models that stretch across and blend digital and physical realms.
PwC sees web3 as a fundamental shift that results in a truly decentralized ecosystem where users have ownership and control of their assets, enabled by emerging technologies.

What should I know about web3?
At the heart of web3 is the concept of decentralized ownership, currently facilitated by blockchain technology. The distributed ledger establishes a verifiable and traceable way to ensure that items and assets are authentic. It also introduces a way to compensate individuals for their time, data and input — while permitting them to retain control of their personal data. An advertiser, for example, might offer consumers some form of currency if they’re willing to share income information.
Suddenly, it’s possible to pay or reward customers and brand devotees for helping to collaborate on a new product or service, whether it’s a clothing line or an eye-catching label for a soft drink bottle. It’s also possible to buy, sell and exchange digital NFTs, as well as tokens representing a “deed” of property in the physical world or digital sports cards in a virtual NFT gallery.
There are three primary components to web3:
- Ownership: Until web3, tokenization was available only at the point of contact for a specific transaction or an ongoing interaction. This imposed limits on what’s possible online. However, blockchain allows for an entirely new ownership model. In this new world, digital assets become more like physical assets. People can take their digital assets wherever they go and transfer those assets to others at any time. A movie or book bought online can suddenly be sold to a friend, a transaction that has to be done physically at the moment.
- Aligned incentives: Web3 supports tighter alignment between brands and consumers through the ownership of digital property. The importance of this shouldn’t be ignored. In a web3 world, one-way connections, and things like linear subscriptions, go away. Consumers are suddenly partners and even owners. With a stake in the web3 world, a business suddenly has an opportunity to create a new and more actively involved type of brand advocate. A social media influencer, for instance, might choose to promote a brand or product on their individual platforms because of incentives that extend beyond money — maybe influence on how a company is run, equity or co-branding opportunities.
- Community: It’s tempting to think of community as an entirely separate entity from ownership and aligned incentives. In reality, the three are deeply intertwined. Incentives and rewards created through tokenization produce a new and potentially more valuable community. Businesses that get this equation right may have an opportunity to achieve a new class of super-loyalty. Collaborative communities can generate art, videos, photos and online posts that aid marketing teams and web creators in developing a brand. No less important: Members of a community are likely to increase their transactions in the physical world.

How a web3 environment could work
- An individual has the option of sharing data one time, for a specified period or into perpetuity. The compensation level from the counterparty could change with the choice. However, if this person decides to reclaim the data, he or she could do so — also at a cost.
- All aspects of the transaction — information to be shared, coins to be granted, reclaiming terms — are codified in a smart contract that is auto enforced by the blockchain.
- Coins/tokens could also be given for performing services needed to operate web3 like reporting bugs or validating transactions.
- Similar to current cryptocurrencies (such as bitcoin where an individual receives bitcoin for helping validate the bitcoin network), web3 will use this concept in legacy web2 services while relying on the new decentralized and incentive mechanisms.
What could web3 look like?
Consider the loyalty programs of today. Customers are limited to using their loyalty rewards on an existing platform. They have the ability to spend their rewards for additional services or products only from that brand. A web3-based loyalty program opens up the possibilities for what can be done with loyalty rewards enabling direct ownership, and the ability to sell to other users in exchange for a currency. This is mutually beneficial for all parties involved — the brand, the seller and the buyer. This invites new users into the marketing funnel and drives additional revenue and demand for the brand through the collection of secondary sales revenue.
In web3, it’s possible to hold objects in both physical and virtual spaces. It’s also possible to transfer digital assets, including NFTs, to create new, enhanced and reinvented types of ownership — and new business models. Trust is built into the system through technologies like blockchain.
Inserting this type of ownership model into the internet has the potential to change the way consumers and brands interact. Suddenly, online spaces more closely parallel the physical world. Web3 also has the potential to alter business-to-business (B2B) partnerships by linking goods and services in ways that weren’t possible in the past.
Web3 is in its infancy. Over the next few years, we expect a company's online presence to become heavily dependent on digital ownership and transactions — for everything from one’s digital identity and virtual real estate to supply chain and social networks.
Why web3 is disruptive and what to consider next
Although the foundations of web3 technology already exist, it will take time for individuals and organizations to put it into motion. Here are a few things to consider.
- Web3 is coming fast, so become familiar with it. Web3 innovation is taking place rapidly. Once organizations understand how to use it and see success in test projects, adoption is expected to accelerate. Companies that understand the technology and use it effectively can gain an advantage in much the same way that certain brands have tapped influencers and social media to achieve big gains. For now, business and technology leaders can benefit from familiarizing themselves with web3 and developing a strategy to capitalize on the opportunity it presents.
- Web3 can change how governance and oversight occur. By its decentralized nature, the need of a third party to oversee operations is gone. Much like how cryptocurrency works today, web3 has the potential to be self-regulating and self-monitoring just by virtue of how the protocols are created. Regardless of what level of involvement your company is considering, you should get to know how the infrastructure of a web3 world could work and what you should do to get comfortable with it.
- There’s a need to rethink and rewire brands and relationships. Web3 represents more than an incremental change in the way brands and consumers interact. Business leaders should rethink and expand how they view relationships and prioritize authenticity. Among other things, web3 introduces a true two-way channel with each customer, providing several avenues to participate with the company. This makes it possible to buy things from them while also selling things to them. Companies have the opportunity to view brand advocates as partners rather than consumers or subscribers.
- Web3 introduces new income sources and new business models. While there’s an opportunity for increased revenue streams through the initial sale of digital goods and services, this is just part of the picture. There’s also an opportunity to realize residual value in perpetuity as NFTs and other assets are bought and sold downstream. The most obvious examples revolve around art or music, where a creator is compensated every time one of his or her creations changes hands. In some cases, this can produce a perpetual source of revenue. Other concepts to keep an eye on are token-based loyalty programs that allow individuals to buy and sell their points or currency; NFTs that serve as access tokens for products, services or value-added components; and blockchain-enabled supply chains that introduce a single source of truth among multiple firms.
- In order to achieve gains, you’ll probably need to step outside your comfort zone (or at least rethink some things). One of the consequences of web3 and a new approach to ownership is that customers suddenly have greater control over things like loyalty points and NFT assets. This may seem jarring to business leaders who are accustomed to retaining complete control over their assets and the people creating them. Other areas to think about include ethics, privacy and cybersecurity. While blockchain authenticates transactions, it doesn’t eliminate the possibility that something like malware or poorly functioning technology could undermine a web3 business model.
While buffeted by the recent market downturn and bankruptcies, digital assets and the technologies underlying them still have the potential to transform business models across sectors.
The evolution of the web

The three epochs

Web2 to Web3 alternatives
